A smart village is a village that is able to manage resources and assets to develop new opportunities, both traditional and digital technology so as to create telecommunications, innovation and better use of knowledge. The purpose of the smart village program is to accelerate the transformation of village development that is powerful, independent, prosperous, and democratic through the use of technology.
Legal basis
Law No. 6 of 2014 Article 78 concerning Village Development
Village development aims to improve the welfare of the village community and the quality of human life as well as poverty alleviation through the fulfillment of basic needs, the development of village facilities and infrastructure, the development of local economic potential, and the sustainable use of natural resources and the environment.
Village development includes the planning, implementation, and supervision stages
Village development as referred to in paragraph (2) prioritizes togetherness, kinship, and mutual cooperation in order to realize the mainstreaming of peace and social justice.
The benefits of a smart village include increasing community awareness, knowledge and skills in the use of digital technology, utilizing technology so that a smart economy can be realized and increasing digital infrastructure facilities to achieve smart mobility in the village. The six pillars of a smart village are smart society, smart economy, smart governance, smart environment, smart life and smart mobility.
Smart communities are people who are able to optimize social capital to strengthen the existence of village social forums, the spirit of self-reliance, and empowerment of women and other marginal groups in the village. In this case, it is an investment in skills and basic knowledge of using the internet effectively to foster creativity and prosperity. One form of this is capacity building training for the community and village officials by utilizing technology.
Smart governance, namely the use of digital technology to support the availability of basic services and public services effectively. Governance that emphasizes the capacity of village apparatus, village institutional capacity, and adequate basic service delivery capacity. Smart governance consists of several indicators, namely the implementation of basic services, the capacity of village institutions and the capacity of the village apparatus. One manifestation of smart governance is the ease of obtaining public services using digital technology such as applications, websites and so on.
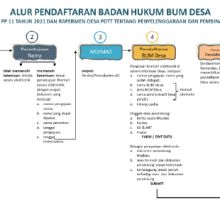
The smart economy in a smart village is the application of digital technology that is used as a tool in market access and information sources, production lines to village distribution. A village economy that is strengthened by economic institutions and equal access to village economic resources that are well managed, focusing on the benefits that can be enjoyed together
and sustainability. One of its forms is the use of technology as a tool in the development of BUM Desa business, the existence of cooperation carried out by the village with various parties to develop economic activities in the village.
Smart Environment, namely digital technology as a means of supporting environmental sustainability goals through conservation and efforts to raise awareness of the use of digital technology as a medium for promoting sustainable and efficient natural resources. Management of the village natural environment prioritizes the principles of sustainability and responsiveness to disaster risk prevention and management. This serves as an effort to meet the needs of local communities, such as information on energy consumption and pollution exposure, community involvement in environmental activities as well as in renewable energy management and the use of sustainable innovative technologies. The forms of environmental application include waste management and waste management.
Smart Life is centered on investing in human resource development and socio-cultural development with the hope of creating a good quality of life in terms of the availability and quality of public services, such as culture, education, health, safety, housing and so on. Quality intelligent life also supports life and social inclusion in rural communities. Examples of intelligent life can be applied to health services, disability and so on.
Smart mobility is the application of digital technology with the hope that digital technology can improve the connectivity of rural areas with other regions in Indonesia. Village communities are expected to be given the convenience of getting services, such as the availability of internet network infrastructure and an innovative and safe transportation system for the community.